Unit 12: Molecular Genetics and Technology
CONCISE Notes
(https://quizlet.com/_1e9xvb)
1.
Deoxyribonucleic acid – DNA
– genetic material that controls the production of proteins; a kind of nucleic
acid
a. Made
of nucleotides, the building blocks
of nucleic acids (see unit 5)
i.
Structure
1. 5-carbon
sugar – deoxyribose – a simple sugar
2. Phosphate
group
3. Nitrogen base
a. Two
kinds
i.
Purines – double rings
1. Adenine
2. Guanine
ii.
Pyrimidines – single ring
1. Thymine
2. Cytosine
ii.
Double helix – twisted ladder shape - two strands that are twisted together –
double-stranded
iii.
Backbone (sides of the ladder) - made of
phosphate and sugar
iv.
Complimentary base pairs – Rungs of the ladder - two strands are bonded together between
nitrogen bases by hydrogen bonds
2. Guanine
only bonds with Cytosine (G-C)
i. Chargaff's Rule - equal amounts of Adenine and Thymine, and equal amounts of Guanine and Cytosine
3. The
complementary bases are held together by weak hydrogen bonds (see unit 5)
4. In
any strand of DNA, there should be equal amounts of complementary base pairs –
same amount of Adenine compare to Thymine…
v.
One chromosome is made of one long strand of DNA
1. Gene
– section of DNA that carried the information to make one protein
a. Proteins
determines the activities of the cell – very important!
2. One
chromosome may have more than 1,000 genes on it
b. The
order of the nucleotides is what determine the kind of allele which then determines
an organisms traits
i.
A-T-T-G-A-C carries different information
from a sequence of T-C-C-A-A-A.
c.
Discovered in 1953
i.
James Watson and Francis Crick - discovered the structure and shape (double helix) of
DNA
ii.
Rosalind Franklin – discovered sugar and
phosphate molecules make up backbone; DNA is made of two strands
2. Central Dogma of Molecular Biology –
Francis Crick
a. The
information contained in DNA is transferred to RNA, which is then transferred
to proteins
b. Once
the information is in the form of a protein, it cannot be changed
c. Three
processes transfer the information stored in DNA: DNA replication,
Transcription, Translation
i.
DNA ↓ → RNA → Proteins
DNA
1. DNA
can be copied = replication
2. DNA
information is stored in RNA = transcription
3. RNA
used to make proteins by ribosomes = translation
3.
DNA Replication – making a
copy of the DNA (duplicating the chromosomes)
a. Occurs
in the nucleus during the S stage of Interphase
b. Process:
i.
The DNA unwinds
ii.
The enzyme DNA
Helicase separates (unzips) the complimentary base pairs
iii.
Free DNA nucleotides in the nucleus bond to the
base pairs of the unzipped DNA strands
iv.
The enzyme DNA
Polymerase bonds the sugar and phosphate groups of the new sides of the DNA
v.
Two new molecules of DNA are formed, each
consisting of one original side of the DNA and one new side of the DNA formed
from the free nucleotides
4.
RNA –
ribonucleic acid; a kind of nucleic acid (see unit 5)
a. Structure
i.
Phosphate group
ii.
Made of ribose sugar instead of
deoxyribose
iii.
Single-stranded instead of
double-stranded
iv.
Guanine and Cytosine bond together (G-C)
v.
Adenine and Uracil bond together, instead
of Adenine and Thymine (A-U)
b. 3
Types
i.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) – takes the information stored on DNA from the nucleus to the
cytoplasm
ii.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – RNA that makes up ribosomes – assemble proteins from amino
acids
iii.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transports amino acids in the cytoplasm to the ribosome to
make proteins
5.
Transcription – copying
the information for one gene found on DNA into a message stored on mRNA; occurs in the nucleus
a. Similar
to DNA Replication but only results in one single strand of RNA; Thymine in not
present in the RNA
b. DNA
cannot leave the nucleus but the information it contains must reach the
ribosomes so they can make proteins
c. Transcription
transcribes the Genetic Code (information needed to make a protein – the
nucleotide sequence) onto mRNA
d. Process:
i.
The DNA unwinds
ii.
An enzyme separates (unzips) the complimentary
base pairs
iii.
Free RNA nucleotides in the nucleus bond to the
base pairs of one gene on one side (the transcription unit)
of the unzipped DNA strands
1. if
the DNA strand were AGC-TAA-CCG, then the RNA strand would be UCG-AUU-GGC
iv.
The new RNA strand breaks away from the DNA
strand and leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores and enters the
cytoplasm
v.
An enzyme zips up the DNA strand
6.
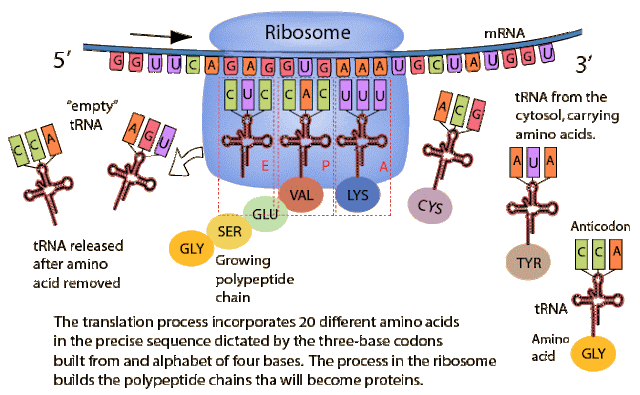
Translation
– changing the message stored on mRNA into a protein; occurs in the cytoplasm at a ribosome
a. Proteins
are made of amino acids
i.
There are 20 different kinds of amino acids
ii.
The order of nitrogen bases in mRNA determine
the order of the amino acids that make a protein
iii.
Codon – the three nitrogen bases of mRNA that
make one amino acid
1. Start
codon – starts the production of a protein (AUG)
2. Stop
codon – stops the production of a protein (UAA)
iv.
Universal Genetic Code – all organisms use the
same genetic code for amino acids and assembling proteins
b. The
message on mRNA must be translated into the language of proteins
c. Process
i.
A ribosome (rRNA) attaches to the mRNA strand
ii.
The ribosome reads the sequence a codon (three
bases) at a time, beginning with the start codon
iii.
tRNA carries carry amino acids to the
ribosome.
1. Anticodon
- three nucleotide sequence that will form base pairs with the codons of the
mRNA.
a. Example
– if the mRNA codon has the sequence AUC, then the tRNA anticodon would be UAG.
iv.
The ribosome attaches the amino acids brought
from the tRNA in the order it received from the mRNA and a peptide bond forms
between amino acids
v.
This repeats until it reaches the stop codon
vi.
A chain of amino acids called a polypeptide (protein) is complete and
released into the cytoplasm
7.
Mutations – mistakes in DNA sequencing; some
mistakes are small and are never noticed, some cause lots of problems; some may
be beneficial
a. Most
occur during DNA replication; if
mutated cell is gamete (meiosis), then the mutation may be inherited
b. Chromosome Mutations – the chromosome
or numbers of chromosomes change
i.
Deletion - when a piece of a chromosome
breaks off
ii.
Duplication - when a broken piece
reattaches to a sister chromatid and causes a duplication of genetic
information in one chromatid.
iii.
Inversion - the broken parts reattach
backwards.
iv.
Translocation - when the broken parts
attach to a non-homologous chromosome.
v.
Nondisjunction – if, during meiosis, the
homologous chromosomes do not separate, then one sex will have an extra
chromosomes (trisomy) and another sex cell will be missing a chromosome
(monosomy); fertilization of these sex cells results in trisomy or monosomy in
the individual
1. Karyotype
- is a chart of chromosomes used to determine if there is an unusual number of
chromosomes
a. Amniocentesis
– removing a small amount of amniotic fluid from around the fetus to obtain
chromosomes for karyotyping
b. Genetic
counseling -
c. Gene Mutations (Point Mutation) – one gene is changes, which causes a change in
what protein is made
i.
Substitution - One nucleotide is substituted for another one. – Changes one amino acid
1. Ex
– The Dog Bit The Cat
2. The
Dog Bit The Car
ii.
Deletion - One nucleotide is deleted from the
strand.
1. Ex
– The Dog Bit The Cat. (delete a g)
2. The
Dob Itt Hec At
iii.
Insertion - One nucleotide is inserted into the
strand.
1. Ex
– The Dog Bit The Cat. (add a g)
2. The
Dog Gbi Tth Eca t
iv.
Deletion
and insertion mutations are also
called Frameshift Mutations
because after the mutation, all of the codons shift, dramatically changing the
protein. – Many amino acids are changed.
v.
Mutagens – external agents that cause gene
mutations; radiation and some kinds of chemicals
1. Carcinogens
– mutagens that cause cancer
a. UV
radiation, x-ray radiation, tobacco, asbestos, benzene
8.
Molecular Genetics – studying and making changes
in DNA
a. Genetic
engineering – changing an organisms DNA
b. Analyzing
DNA
i.
DNA extraction – separating the DNA from the
rest of the cell
1. Process
a. Cut
the DNA into smaller pieces using restriction enzymes
b. Gel
electrophoresis – separate the pieces of DNA
i.
Place the DNA fragments in a chamber filled with
a special gel
ii.
Electricity is applied to the chamber, and
negatively charged DNA moves toward the positive end of the chamber
1. Smaller
fragments move faster than larger ones
2.
A pattern is created on the gel
ii.
DNA Fingerprinting – the separated DNA fragments
are compared to another sample of DNA
1. The
pattern is unique to the person
2. Can
identify criminals or see if two people are related
c. Recombinant
DNA – combining DNA from one organism with another
i.
Transformation – placing the recombined DNA back
into a living cell
1. In
medicine, human DNA is placed into bacteria
a. Defective
genes can be replaced by normal ones
i.
Diseases caused by single genes, such as
Huntington’s disease, Cystic Fibrosis, and Sickle cell anemia, can be treated
b. Insulin
is made in this way
ii.
Process
1. Restriction
enzymes cut a gene from human DNA that makes insulin
2. The
human DNA is placed into the bacteria plasmid (bacteria DNA)
3. The
bacteria grow and reproduce with the human gene making insulin
d. Transgenic
Organisms – organisms that contain genes from other organisms
i.
Cows – extra genes that produce growth hormones
cause the cows to grow larger and faster
ii.
Plants – make plants more resistant to disease
and pests, so crops and be grown without chemicals and insecticides
iii.
Disadvantages
1. Cross
pollination with wild plants could produce plants that cannot be controlled
with weed killers or that would be harmful to beneficial insects
2. Effects
of the extra growth hormones on humans is unknown
3. Possible
spread of the transformation genes used into the environment could cause
bacteria to become antibiotic resistant
e.
Reproductive Cloning – making a copy of an organism
i.
Process
1. Transferring
DNA from a donor cell into an egg that has had its nucleus removed
2. Chemicals
or electricity cause the nucleus to enter mitosis and divide
3. The
egg is implanted into the uterus of a female
4. The
cloned organism develops and is born as if it was natural
ii.
The cloned organism is identical to the donor
and can be used in medical research
iii.
Some scientists are working on ways to save endangered species
f.
Selective Breeding
i.
Using the plants or animals that have the
desired traits as the parents for the next generation
ii.
Have been used for centuries
9.
Reading Codon Charts
a. A
codon chart determines what amino acid will be brought to the ribosome by
translating the mRNA codon
b. tRNA
has the anticodon and carries a specific amino acid
c.
Circle Codon Chart
i.
How to Read a Codon Chart
1. Read
the mRNA codon – eg. GUA
a. You
may have to convert the DNA sequence to the mRNA code
2. Start
in the middle of the chart – G
3. Move
to the next row – U
4. Move
to the outer row – A
5. The
Amino Acid associated with the codon GUA is Valine
d. Square
Codon Chart
i.
How to Read a Codon Chart
1. Read
the mRNA codon – eg. GUA
a. You
may have to convert the DNA sequence to the mRNA code
2. In
the first column, find G
3. Move
to middle columns and follow G to the U
4. Read
across from A in the third column to find the amino acid – Valine
10.
Interesting Human Genetic Mutations
a. Tetrachromacy – found on X chromosome - increase
in the range of colors the eye can see – most people have 3 cones to see
colors, 12% of women have 4
b. Marfan Syndrome – MFS1 gene mutation - abnormally
tall and highly flexible; may develop weakened connective tissue; heart, eye,
blood vessel problems
c. Unbreakable
bones – LRP5 gene mutation on chromosome 11 that increases bone density; also
can’t swim and has bone growths in roof of mouth
d. Super
Pain Tolerance – MCR1 gene – produces red hair, and sometimes a high tolerance
for pain and spicy foods
e. Super
Sleeplessness – DEC2 gene mutation – sleep far less than other people
f.
Distichiasis – two rows of eye lashes on each
eye lid – Actress Elizabeth Taylor had this mutation
g. Super
Strength – mutation causes an increase in the size of muscles by suppressing a
protein that limits muscle growth














No comments:
Post a Comment